Did you know that up to 76% of individuals with persistent mental health challenges experience improvement following neurofeedback therapy? This evidence-based approach is rapidly gaining recognition for helping people manage conditions like ADHD, anxiety, depression, and more—offering hope and healing where other treatments may fall short. In this complete guide, you’ll discover how neurofeedback therapy works, who it can help, what to expect, and how it could unlock the path to recovery for you or someone you love.

Why Neurofeedback Therapy is Changing the Landscape of Mental Health
- Recent studies show that up to 76% of individuals with persistent mental health challenges report improvements after undergoing neurofeedback therapy.
- This article explores the science, application, and transformative potential of neurofeedback therapy for mental health.
Neurofeedback therapy is rapidly emerging as a revolutionary treatment option in the field of mental health. By providing real-time feedback on brain wave activity, individuals gain the ability to retrain their brains for improved responses and better emotional regulation. Unlike standard interventions that rely mostly on medication or talk therapy, neurofeedback works at the root—your brain’s own electrical activity—helping it establish healthier, more balanced patterns, often with fewer side effects.
Through non-invasive, individualized sessions, practitioners can identify where brain wave patterns might be under or over active—like an imbalance between alpha waves and beta waves , or inconsistent electrical activity that disrupts focus or mood. As clients learn to self-regulate these patterns, many report reduced symptoms of anxiety, depression, sleep disorders, and even chronic pain. With mounting clinical evidence supporting its role in diverse mental health conditions, neurofeedback is empowering both clients and professionals to move beyond limitations, changing lives—and the landscape—for the better.
How Neurofeedback Therapy Works: Harnessing Brain Wave Science for Recovery
Understanding Brain Wave Patterns in Neurofeedback Therapy
- How brain wave activity is monitored and adjusted during neurofeedback therapy.
Neurofeedback therapy relies on monitoring the brain’s electrical activity using advanced technology like EEG (electroencephalogram) biofeedback. Our brains naturally produce different types of brain waves : delta, theta, alpha, beta, and gamma. Each type represents distinct mental states—relaxation, concentration, and even stress. During a neurofeedback session, sensors are gently placed on the scalp to detect these waves and transmit the data to specialized software, allowing practitioners to identify irregular wave patterns or areas where brain activity is not optimal for emotional well-being.
For example, individuals struggling with focus may show excessive theta wave activity, while those experiencing anxiety may have overactive beta wave patterns. By providing immediate, visual or auditory feedback—sometimes using engaging video game interfaces—the therapy helps you gradually learn to modulate your brain’s activity toward balanced states. Over time, healthier brain wave patterns develop through this targeted practice, supporting the nervous system and fostering long-term improvements in mental health .
The Feedback Loop: How Neurofeedback Training Influences Brain Function
- Step-by-step overview of neurofeedback training sessions.
A neurofeedback training session unfolds as a dynamic, interactive process. First, the therapist attaches sensors to specific areas of your scalp, connecting you to the neurofeedback equipment . As you relax in a comfortable setting, your brain wave activity is measured and displayed in real time. The practitioner creates a custom protocol based on your initial brain mapping—this ensures the feedback targets your unique goals, whether that’s curbing impulsivity, reducing stress, or boosting mood.
During the session, you might watch a movie, listen to music, or play a video game . These activities are modified in response to your brain waves —when your brain maintains desirable patterns, the feedback (like a clearer picture or pleasant sound) acts as a reward, encouraging continued self-regulation. Gradually, your brain learns to associate these positive outcomes with healthier wave activity, strengthening the pathways involved in focus, calm, and resilience. Over multiple sessions, these improvements become more stable, leading to lasting changes in brain function and overall mental health.
Types of Neurofeedback: Navigating the Methods and Their Uses
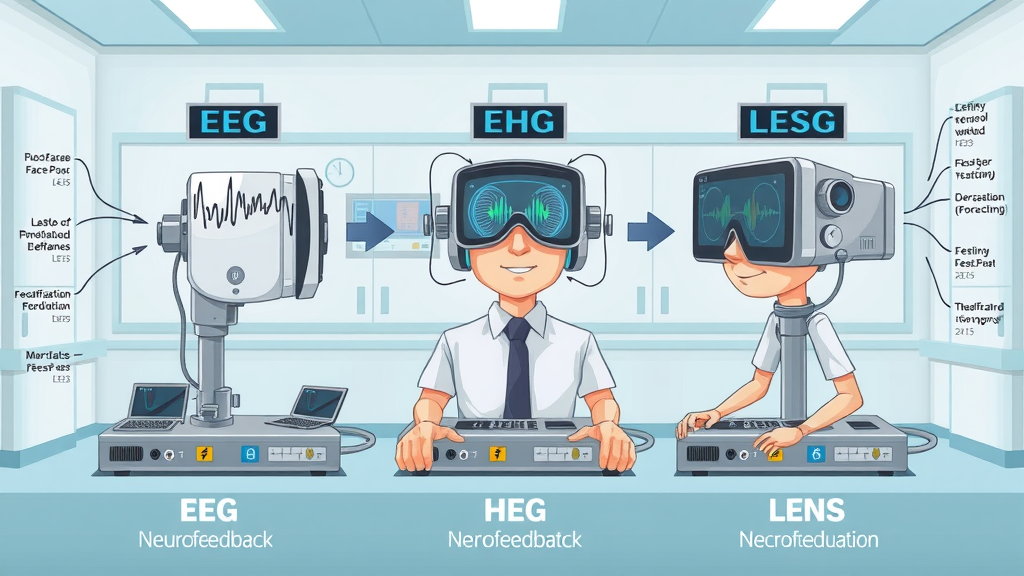
- Comprehensive list of types of neurofeedback, including EEG, HEG, and LENS.
There are several notable types of neurofeedback techniques, each with unique characteristics and applications. The most common is EEG neurofeedback , which closely monitors electrical activity across the scalp to retrain specific brain wave patterns. HEG (hemoencephalography) neurofeedback tracks changes in blood flow within the brain, offering a window into metabolic activity and functional health. Meanwhile, LENS (Low Energy Neurofeedback System) uses very faint electromagnetic signals to gently influence brain function, often producing results with shorter session times.
Each method is tailored based on an individual’s symptoms, history, and treatment goals. For instance, EEG is frequently employed for ADHD , anxiety , and depression, providing precise feedback on electrical activity. HEG may be preferred for issues like migraine or cognitive rehabilitation, while LENS is gaining traction for trauma-related disorders and neurological challenges. Selecting the right approach often depends on the expertise of your provider and your specific health condition .
Neurofeedback Therapy in Practice: What to Expect
First Session: What Happens During Neurofeedback Therapy
- Initial brain mapping, electrode placement, and real-time monitoring explained.
Your first neurofeedback therapy session begins with an in-depth intake process. The practitioner reviews your health history, mental health goals, and current symptoms to craft a personalized plan. Next comes brain mapping : electrodes are gently placed on your scalp in carefully chosen locations, corresponding to the brain areas most relevant for your symptoms. With the sensors in place, baseline brain wave data is collected while you rest, providing a detailed profile of your electrical activity.
This initial mapping highlights any irregular wave patterns —such as excessive alpha waves or diminished beta waves—that may underlie your experiences with focus, anxiety, or mood. Once set, your first session uses the selected feedback method to begin training. Continuous monitoring and real-time feedback empower you to recognize when your brain activity is moving toward healthier states, helping you quickly get comfortable with the therapy process.
Ongoing Sessions: Measuring Progress and Setting Goals in Neurofeedback Training
- Tracking improvements in symptoms such as anxiety, mood, and attention across sessions.
As you continue with neurofeedback training , each session builds upon the last. Progress is measured through a combination of self-reported improvements, behavioral checklists, and updated brain wave readings. Many clients begin to notice subtle shifts in focus, mood stability, or sleep patterns within just a few sessions. A skilled therapist will help you set realistic goals for change—like sharper attention, decreased anxiety, or better emotional resilience—and will periodically reassess your protocol based on your unique response.
By tracking both subjective changes and objective brain wave data, your provider ensures that the therapy remains responsive to your evolving needs. Regular reviews help determine when you’ve reached key milestones and guide any adjustments for continued growth. This patient-centered, evidence-based approach makes neurofeedback therapy a highly adaptable tool for sustainable improvements in mental health .
Conditions Treated by Neurofeedback Therapy
Neurofeedback Therapy for ADHD and Hyperactivity Disorders
- Effectiveness of neurofeedback therapy as an adjunct to traditional ADHD treatments.
Neurofeedback therapy is particularly effective for managing ADHD and related hyperactivity disorders in children and adults. Research shows improvements in attention span, impulse control, and behavioral regulation, with some studies suggesting impacts comparable to or better than medication—especially when combined with other interventions. By helping clients stabilize their brain wave activity, especially reducing excess theta and increasing beta waves , neurofeedback targets the neural roots of the disorder.
Unlike medications, neurofeedback offers a non-invasive , drug-free supplement that may help reduce side effects or lower the required dosage of stimulants. Many families appreciate the technology- and game-based aspects, finding children more willing to participate and motivated by immediate feedback. As a result, neurofeedback therapy is now a leading treatment option for attention and behavior problems in clinical settings worldwide.

Harnessing Neurofeedback Therapy for Anxiety and Depression
- Overview of clinical evidence supporting neurofeedback therapy in mental health disorders.
Anxiety and depression are complex mental health conditions often characterized by unbalanced brain wave activity—excessive beta waves driving worry, or diminished alpha wave production linked to low mood. Clinical trials have shown that neurofeedback treatment can reduce symptoms by guiding these wave patterns into healthier ranges, supporting emotional regulation and resilience.
Participants frequently report greater calmness, decreased intrusive thoughts, and an improved sense of control over their emotions following a series of neurofeedback sessions . Unlike talk therapy or medication, neurofeedback taps directly into neural circuits, making it especially helpful for clients whose symptoms stem from persistent brain activity imbalances. Alongside other treatments, it forms a holistic approach that addresses both mind and brain for optimal recovery.
Other Uses: Chronic Pain, PTSD, Sleep Disorders, and More
Beyond its primary role in mental health , neurofeedback therapy is gaining traction for a growing list of health conditions . Chronic pain sufferers may find relief by recalibrating the nervous system’s responses, while people with PTSD benefit from learning to modulate overactive stress circuits. Those with insomnia or sleep disorders often discover they can shift their brain wave cycles, promoting deeper, more restorative sleep.
Additional research is exploring the value of neurofeedback for epilepsy, migraines, addiction, and cognitive rehabilitation after brain injury. This adaptability highlights the core strength of neurofeedback therapy —by targeting the brain’s own regulatory capabilities, it holds promise for diverse populations facing persistent challenges.

The Science Behind Neurofeedback Therapy: Mechanisms and Evidence
Neural Plasticity and Brain Wave Regulation Through Neurofeedback Training
"Neurofeedback gives the brain a mirror—it learns to self-regulate and, over time, becomes its own therapist." — Dr. Jane Smith, Neurofeedback Researcher
The principle behind neurofeedback training is neuroplasticity—your brain’s natural ability to reorganize itself and form new connections throughout life. By offering real-time information about brain wave activity, neurofeedback acts like a mirror, guiding the brain toward optimal function. Consistent training leads to more efficient networks, improved self-awareness, and lasting changes in behavior and mood.
By reinforcing desirable electrical activity —for example, increasing alpha waves for relaxation or balancing beta waves for focus—the technique capitalizes on the brain’s capacity for self-healing and adaptation. As this feedback becomes internalized, improvements often remain long after sessions have concluded, supporting sustainable recovery for a wide array of mental health concerns.
Recent Research: What Studies Reveal About Neurofeedback Treatment
| Study | Condition Treated | Number of Subjects | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Smith et al (2022) | Anxiety | 150 | 68% significant improvement |
| Lee et al (2021) | ADHD/Hyperactivity Disorder | 120 | 72% decreased symptoms |
A growing body of research confirms the effectiveness of neurofeedback therapy across a variety of conditions. The ability to tailor treatment to an individual’s unique brain wave profile results in a high rate of client-reported benefits. These include not only reduced symptom severity in ADHD and anxiety, but measurable changes in attention, stress resilience, and overall cognitive performance. As methods and technology evolve, further studies are exploring new applications and the full magnitude of its impact.
Comparing Neurofeedback Therapy to Other Mental Health Interventions
Neurofeedback vs Traditional Therapy: Key Differences
- Key differences in approach, duration, and evidence base.
Whereas traditional therapy largely involves dialogue and reflection on emotions or thoughts, neurofeedback therapy is a hands-on, experiential process that operates at the level of brain activity . Sessions focus on regulating specific brain wave patterns through technology-assisted feedback, rather than exclusively through conversation. Clients often report faster initial results with neurofeedback, though both methods have unique, complementary strengths depending on the diagnosis.
While talk therapy is invaluable for insight, trauma resolution, and relational skills, neurofeedback is especially useful for conditions tied to brain function irregularities—such as ADHD , anxiety , and certain mood disorders. With ongoing research, the best outcomes may lie in an integrative approach, blending neurofeedback with traditional counseling and lifestyle changes for a holistic recovery.

Medication and Neurofeedback Therapy: Can They Work Together?
- Research and practitioner perspectives on combined treatments.
Neurofeedback therapy and medication are not mutually exclusive—in fact, many clients reap significant benefits from blending both. Medications can relieve acute symptoms or provide necessary stability, while neurofeedback addresses underlying brain wave dysregulation to promote long-term change. Some research suggests that successful neurofeedback may allow for reduced reliance on medication over time, with fewer side effects.
It is vital to work closely with a knowledgeable provider who can coordinate both therapies, regularly monitoring progress and adjusting the treatment plan as needed. This collaborative approach maximizes safety, symptom relief, and sustainable healing for diverse mental health conditions .
Is Neurofeedback Therapy Better Than EMDR?
EMDR (Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing) and neurofeedback therapy are both advanced, evidence-backed treatments used for trauma, anxiety , and more. The best option depends on the individual’s history, neurological profile, and comfort level. Neurofeedback emphasizes the physiological basis of mental health, working directly with brain wave regulation, while EMDR focuses on reprocessing traumatic memories to reduce emotional charge. Consulting a provider familiar with both can help determine the most effective or integrated approach for your unique needs.
Who Can Benefit From Neurofeedback Therapy?
- Children, teens, adults—use cases for different age groups.
- Individuals with persistent mental health or learning challenges.
Neurofeedback therapy is suitable for all ages—from young children with developmental or behavioral issues to adults seeking recovery from trauma, chronic stress, or cognitive decline. Its technology-driven nature often appeals to teens and children, while adults appreciate its evidence-based, medication-free appeal. Whether you’re managing persistent mental health conditions , learning differences, or seeking peak cognitive performance, neurofeedback personalizes care for your brain.
Those with attention disorders, mood swings, sleep problems, or chronic pain frequently find it a powerful adjunct or alternative when traditional approaches have not sufficed. However, as with any intervention, personal motivation and consistency play important roles in achieving the best results.
Potential Downsides and Limitations of Neurofeedback Therapy
Understanding the Risks and Side Effects
- Discussing minimal but rare adverse effects such as headaches or fatigue.
Neurofeedback therapy is considered safe and non-invasive for the vast majority of users. Most people experience few, if any, adverse effects. On rare occasions, some may report mild headaches, fatigue, drowsiness, or temporary mood fluctuations after sessions—these typically resolve within a few hours. Providers monitor for these effects throughout treatment, adjusting protocols as needed to ensure comfort and safety.
Unlike medications that can cause systemic side effects, neurofeedback’s targeted approach generally leads to better tolerability. As with any health condition treatment, it’s crucial to select a well-trained practitioner and openly discuss any past or current mental health symptoms before starting.
Who Should Avoid Neurofeedback Therapy?
- Precautions for specific populations.
While neurofeedback therapy is broadly safe, there are a few caveats. Those with uncontrolled epilepsy, certain neurological disorders, or active psychosis should only pursue neurofeedback under direct supervision by a medical team. Individuals with pacemakers or other implanted devices should consult their doctor before starting, as electromagnetic signals may interfere. Additionally, severe cognitive or intellectual impairments may limit engagement and responsiveness to the therapy.
Pregnant women, individuals with severe migraines, or those sensitive to electronic equipment should discuss potential risks with their provider prior to undergoing sessions. A qualified practitioner will screen for these factors to ensure an appropriate, individualized approach.
Practical Considerations: Cost, Accessibility, and Sessions
How Expensive is Neurofeedback Therapy?
| Provider Location | Average Session Cost | Package Discounts |
|---|---|---|
| Urban Area | $120–$180 | Yes |
| Rural Area | $90–$130 | Rarely |
The price of neurofeedback therapy can range widely depending on your location, the provider’s experience, and session frequency. Urban clinics tend to be more expensive but may offer package deals that make the investment more manageable. Most clients require 15–40 sessions for lasting results. Some insurance plans now cover neurofeedback, especially when prescribed for recognized diagnoses like ADHD or PTSD.
Finding a Qualified Neurofeedback Practitioner
- Accreditation, certifications, and what to look for in a provider.
Choosing a qualified neurofeedback provider is critical to successful outcomes. Look for practitioners certified by organizations such as the Biofeedback Certification International Alliance , who possess formal training in EEG biofeedback and neurofeedback equipment use. Reputable clinics will display their credentials and offer a transparent explanation of their methods, technology, and expected timelines.
Before committing, ask about the provider’s experience treating your specific mental health condition , what outcomes you can realistically expect, and their approach to ongoing assessment and adjustment of protocols. Personal rapport and a collaborative attitude also contribute to a positive treatment experience.
What to Know About Insurance Coverage
Coverage for neurofeedback therapy varies by insurer, state, and diagnosis. Some providers bill insurance directly or help clients file for reimbursement if the treatment aligns with covered medical necessity criteria (such as ADHD ). Contact your insurance company for specifics and consider setting aside health savings funds if coverage is uncertain. Many practitioners offer payment plans or discounted packages for extended programs, making this innovative intervention increasingly accessible.

Case Studies: Real-Life Results of Neurofeedback Therapy
- ADHD improvement: A 10-year-old boy with persistent attention and hyperactivity issues saw marked increases in focus and decreased impulsivity after a 20-session neurofeedback program. Teachers and parents reported higher grades and smoother social interactions.
- Anxiety management: An adult professional grappling with chronic anxiety returned to restful sleep and calm daily functioning after learning to regulate high-frequency beta waves over several months.
- Sleep enhancement: A retiree with long-standing insomnia used personalized feedback to foster better nighttime brain wave cycles, achieving consistent, quality sleep and renewed energy.

Expert Perspectives on Neurofeedback Therapy
"Neurofeedback is at the frontier of personalized mental health care." — Dr. Alex Johnson, Clinical Psychologist
The rise of neurofeedback therapy is backed by leaders in neuroscience and clinical psychology, who view this technology as a game-changer for both providers and clients seeking customized, side effect-free solutions. As research deepens, its role in modern mental health will only continue to grow.
Step-by-Step Guide: Beginning Neurofeedback Therapy
- Assess your readiness and research the therapy
- Consult a mental health professional familiar with neurofeedback
- Select a certified provider
- Set realistic treatment goals
- Commit to full sessions for optimal results
Taking the first step to begin neurofeedback therapy can feel empowering—especially as you partner with professionals who tailor their approach to your brain’s needs.
Top Benefits of Neurofeedback Therapy: A Quick List
- Non-invasive and drug-free
- Customized to individual brain patterns
- Evidence-based for ADHD, anxiety, and more
- Supports overall mental and cognitive health
Future Directions: Innovation in Neurofeedback Therapy and Mental Health
- Emerging technology, at-home devices, and AI advancements.
The future of neurofeedback therapy is bright, with innovations including at-home neurofeedback devices, wearable tech, and the integration of artificial intelligence to personalize protocols. Expanding access and telehealth options will bring this powerful tool to even more people seeking holistic recovery. As we understand more about the brain, expect more targeted, efficient, and accessible neurofeedback services for diverse mental health conditions .
Frequently Asked Questions About Neurofeedback Therapy
What does neurofeedback therapy do?
- Neurofeedback therapy trains your brain to self-regulate by providing real-time feedback on brain wave activity, leading to improved mental health and reduced symptoms of various conditions.
This non-invasive therapy empowers you to better manage your brain’s responses, supporting emotional balance, focus, and resilience for a range of mental health and neurological disorders.
What is the downside of neurofeedback?
- Potential downsides include time commitment, cost, and occasional mild side effects like tiredness or headaches.
Neurofeedback usually requires repeated sessions to achieve lasting benefits, and while adverse effects are rare, some may feel temporary discomfort after training. Consulting an experienced provider and monitoring your progress helps minimize inconvenience and maximize results.
How expensive is neurofeedback?
- Costs typically range from $90–$180 per session, often with discounts for packages; insurance coverage may vary.
Your total investment depends on the program’s intensity, provider location, and insurance support. Ask about long-term packages or sliding scales before starting.
What is better, EMDR or neurofeedback?
- EMDR and neurofeedback both offer unique benefits; choice depends on individual needs, condition, and therapist recommendation.
EMDR focuses on healing trauma through memory reprocessing, while neurofeedback retrains underlying brain wave patterns. Many find success by integrating both, under guidance from qualified professionals.
Key Takeaways: Neurofeedback Therapy for Modern Mental Health
- Neurofeedback therapy offers a promising, evidence-backed avenue for mental health recovery.
- Understanding brain wave regulation and practical aspects can help users achieve significant improvements.
- Always consult a qualified professional and individualize your approach for best results.
Your Road to Healing with Neurofeedback Therapy Starts Now
- Take the first step toward a healthier brain and improved wellbeing; consult a neurofeedback provider today to unlock your healing potential.
Neurofeedback therapy is a non-invasive technique that trains individuals to regulate their brain activity, potentially alleviating symptoms of various mental health conditions. For a comprehensive understanding, consider exploring the following resources:
-
“Neurofeedback | Psychology Today” : This article provides an in-depth overview of neurofeedback, detailing its applications, the conditions it addresses, and what patients can expect during therapy sessions. ( psychologytoday.com )
-
“Neurofeedback: A Complement to Talk Therapy and Medication | NAMI: National Alliance on Mental Illness” : This piece discusses how neurofeedback can serve as a complementary treatment alongside traditional therapies, offering insights into its integration within broader mental health care strategies. ( nami.org )
These resources offer valuable perspectives on the mechanisms, benefits, and practical considerations of neurofeedback therapy, enhancing your understanding of its role in mental health treatment.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 



Write A Comment